The Hidden Crisis: Why Zinc and Magnesium Deficiency Is Threatening Your Health From the Womb and Beyond
Published: July 1, 2025 | Author: Aaron Smith, Nutritional Biochemist & Funny Dad Joke Teller
Introduction: The Silent Epidemic Affecting Millions
In our modern world of abundant food choices, a paradox exists that threatens the health of millions: we're overfed yet undernourished. While grocery store shelves overflow with options, the nutritional quality of our food supply has been quietly declining for decades. At the center of this crisis are two essential minerals—zinc and magnesium—whose deficiencies are creating a “silent epidemic” with far-reaching consequences for human health.

Recent research reveals that approximately 17% of the global population is at risk of inadequate zinc intake, while magnesium deficiency affects an estimated 50% of adults in developed countries. These aren't just statistics—they represent millions of people experiencing compromised immune function, cognitive decline, and increased disease risk, often without realizing the underlying cause.
The Science Behind Zinc Deficiency: More Than Just a Mineral Gap
Understanding Zinc's Critical Role
Zinc is involved in more biological functions than any other micronutrient, serving as a cofactor in over 300 enzymatic reactions. From DNA synthesis and protein production to immune cell activation and wound healing, zinc is fundamental to life itself. Yet despite its importance, zinc deficiency has been described by leading researchers as “the most insidious” of all micronutrient deficiencies due to its wide-ranging and often subtle impacts.
The Perfect Storm Creating Widespread Deficiency
Two major forces are converging to worsen zinc deficiency rates globally:
1. The Cost-of-Living Crisis and Dietary Shifts
Economic pressures are pushing more people toward high-energy, nutrient-poor processed foods. This creates what researchers call “hidden hunger”—where individuals consume adequate calories but remain deficient in essential micronutrients. The modern Western diet, dominated by refined grains, processed foods, and sugar, is inherently low in bioavailable zinc.
2. Environmental Changes and the “Carbon Nutrient Penalty”
Rising atmospheric CO2 levels are projected to decrease zinc concentration in staple crops like wheat and rice by nearly 15% by 2050. This environmental shift means our food supply is becoming progressively less nutritious, even as we struggle to meet current nutritional needs.
Health Consequences Across the Lifespan
The impact of zinc deficiency varies by life stage but is universally serious:
In Children and Adolescents:
- Stunted growth and development
- Compromised immune function leading to recurrent infections
- Cognitive impairment affecting learning and memory
- Delayed wound healing and poor skin health
In Adults:
- Increased risk of Type 2 diabetes due to zinc's role in insulin function
- Cardiovascular disease risk from impaired lipid metabolism
- Weakened immune response and increased infection susceptibility
- Poor reproductive health and fertility issues
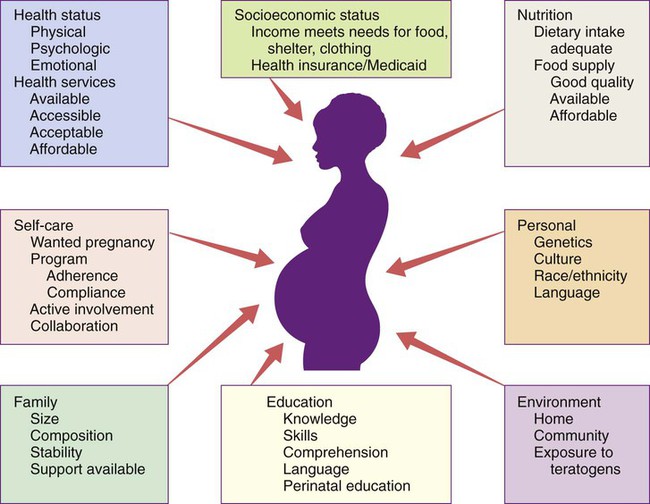
During Pregnancy:
- Increased risk of pregnancy complications
- Impaired fetal brain development
- Higher likelihood of preterm birth
- Compromised maternal immune function
Magnesium: The Forgotten Mineral Powering Your Body
The Scope of Magnesium Deficiency
Magnesium serves as a cofactor in over 300 enzymatic reactions governing energy production, nerve transmission, muscle function, and heart rhythm regulation. Despite its critical importance, magnesium deficiency has become a “silent epidemic,” with symptoms that are often subtle initially but can progress to serious health complications.

Root Causes of Modern Magnesium Depletion
Soil Depletion: The Foundation of the Problem
The most fundamental cause of our magnesium-deficient food supply is the degradation of agricultural soil. Research comparing nutrient data from 1950 to 1999 found that magnesium content in 43 different crops dropped significantly, with some analyses showing that wheat and vegetables have lost as much as 25% of their magnesium content.
This depletion is driven by:
- Industrial monoculture farming practices
- Heavy use of synthetic NPK fertilizers that neglect trace minerals
- Soil erosion and degradation of microbial life
- Depletion rates up to 1,000 times faster than natural restoration
Modern Lifestyle Factors
- High consumption of processed foods stripped of natural minerals
- Increased stress levels that deplete magnesium stores
- Medications that interfere with magnesium absorption
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- High-sodium diets that increase magnesium excretion
The Health Impact of Magnesium Deficiency
Subclinical magnesium deficiency is a major driver of chronic inflammation, contributing to:
- Metabolic disorders including insulin resistance
- Cardiovascular disease and hypertension
- Osteoporosis and bone health issues
- Mental health problems including anxiety and depression
- Chronic fatigue and muscle weakness
- Migraine headaches and sleep disorders
The Power of Synergy: Why Zinc, Magnesium, and Vitamin C Work Better Together
Immune System Fortification
The combination of zinc, magnesium, and vitamin C creates a powerful immune-supporting trio:
Zinc acts as a master regulator of immunity, essential for T-cell development and activation—the white blood cells that destroy virus-infected cells and coordinate immune responses.
Vitamin C stimulates white blood cell production and acts as a potent antioxidant, protecting immune cells from oxidative damage during immune responses.
Magnesium supports overall immune function by regulating inflammatory responses and maintaining cellular energy production needed for immune cell activity.
Cognitive Health and Brain Development
The brain's development and function are exquisitely sensitive to nutrient availability, particularly during critical windows of development:
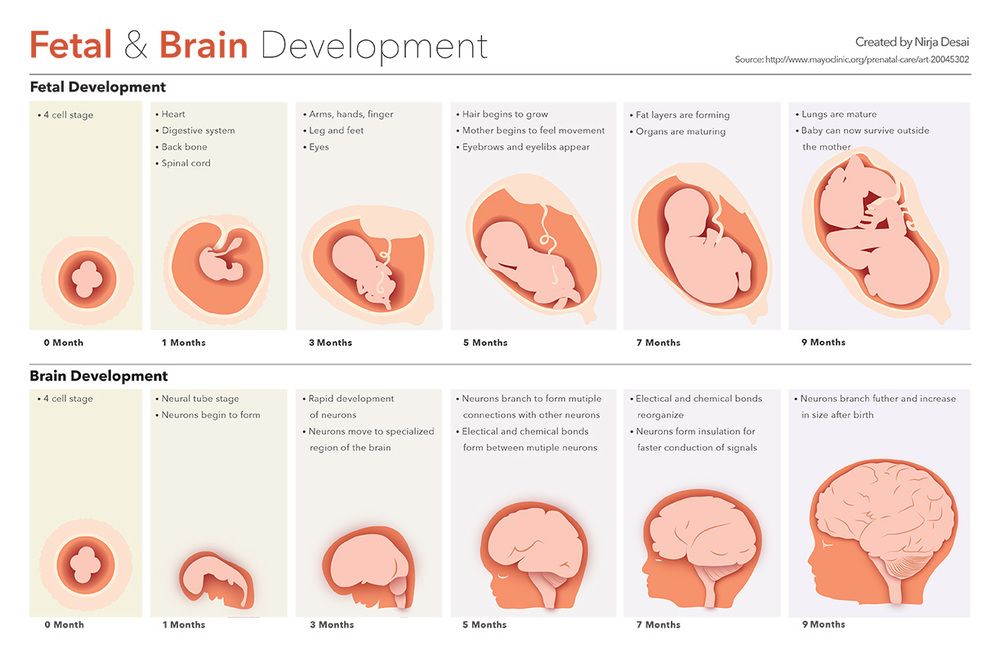
Prenatal Brain Development:
Research in Developmental Origins of Health and Disease (DOHaD) shows that maternal nutrition has lifelong impacts on offspring brain structure and function. Deficiencies in zinc, magnesium, and supporting nutrients can permanently alter cognitive capacity.
- Zinc is vital for neurogenesis (creation of new neurons) and neuronal migration
- Magnesium supports nerve transmission and neurological health
- Iron and other minerals work synergistically to support myelination and hippocampal energy metabolism
Lifelong Cognitive Support:
These nutrients continue to support brain health throughout life by:
- Maintaining neurotransmitter production and balance
- Supporting cellular energy production in brain tissue
- Protecting against oxidative stress and inflammation
- Facilitating memory formation and recall

Cellular Energy Production
At the cellular level, these nutrients are fundamental to energy production:
- Magnesium is essential for ATP synthesis, the body's primary energy currency
- Zinc supports countless metabolic pathways that convert food into usable energy
- Vitamin C protects cellular machinery from oxidative damage during energy production
From the Womb and Beyond: Supporting Health Across the Lifespan
Pregnancy and Early Development
The period from conception through early childhood represents the most critical window for nutritional intervention. During this time, adequate zinc and magnesium intake supports:
Maternal Health:
- Optimal immune function during pregnancy
- Proper hormone regulation and metabolism
- Reduced risk of pregnancy complications
- Faster postpartum recovery
Fetal Development:
- Proper neural tube formation and brain development
- Healthy organ system development
- Optimal birth weight and gestational age
- Foundation for lifelong cognitive capacity
Early Childhood:
- Proper growth and development milestones
- Strong immune system development
- Cognitive development and learning capacity
- Healthy eating patterns and nutrient absorption
Supporting Health Through Life Stages
Childhood and Adolescence:
- Supporting rapid growth spurts
- Maintaining immune function during school years
- Supporting cognitive development and academic performance
- Establishing healthy bone density
Adulthood:
- Maintaining energy levels and metabolic health
- Supporting reproductive health and fertility
- Preventing chronic disease development
- Managing stress and supporting mental health
Aging:
- Maintaining cognitive function and memory
- Supporting bone health and preventing osteoporosis
- Maintaining immune function
- Supporting cardiovascular health
The ThincZinc+ ULTRA Advantage: Bridging the Nutritional Gap
Why Supplementation Has Become Necessary
Given the challenges of obtaining adequate zinc and magnesium from food alone—due to soil depletion, processing, and modern dietary patterns—targeted supplementation has become essential for optimal health. However, not all supplements are created equal.
Superior Bioavailability and Absorption
ThincZinc+ ULTRA is formulated with bioavailable forms of these essential nutrients:
Zinc Glycinate: This chelated form of zinc is bound to the amino acid glycine, enhancing absorption and reducing the potential for digestive upset compared to other forms like zinc sulfate or zinc oxide.
Magnesium Malate: This form combines magnesium with malic acid, supporting both absorption and cellular energy production. Malic acid plays a role in the Krebs cycle, the cellular process that generates energy.
Natural Vitamin C from Camu Camu: Rather than synthetic ascorbic acid, ThincZinc+ ULTRA features vitamin C from Camu Camu, an Amazonian superfruit containing up to 60 times more vitamin C than oranges. Research shows that whole-food sources of vitamin C, with their complex matrix of supporting compounds, are more effective than isolated synthetic versions.
Synergistic Formulation
The nutrients in ThincZinc+ ULTRA are carefully balanced to work synergistically:
- Optimal ratios prevent nutrient competition for absorption
- Supporting cofactors enhance bioavailability
- Comprehensive formula addresses multiple pathways simultaneously

Evidence-Based Benefits and Clinical Research
Immune System Support
Clinical studies demonstrate that adequate zinc and magnesium intake:
- Reduces duration and severity of common cold symptoms
- Supports healthy inflammatory responses
- Enhances vaccine effectiveness
- Improves wound healing and tissue repair
Cognitive and Mental Health Benefits
Research shows that optimal mineral status supports:
- Improved memory and cognitive performance
- Better stress management and mood regulation
- Enhanced sleep quality and duration
- Reduced risk of age-related cognitive decline
Metabolic and Cardiovascular Health
Studies indicate that zinc and magnesium sufficiency:
- Improves insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism
- Supports healthy blood pressure regulation
- Enhances lipid profiles and cardiovascular markers
- Reduces inflammation and oxidative stress
Practical Implementation: Maximizing Your Nutritional Investment
Optimal Timing and Dosage
For maximum benefit, consider these evidence-based recommendations:
- Take with food to minimize digestive upset
- Separate from calcium and iron supplements to prevent absorption interference
- Consistent daily intake is more beneficial than sporadic high doses
- Follow manufacturer's guidelines for your specific product
Complementary Lifestyle Factors
Supplementation works best as part of a comprehensive health strategy:
- Maintain a diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods
- Manage stress through regular exercise and relaxation techniques
- Ensure adequate sleep for optimal nutrient utilization
- Stay hydrated to support nutrient transport and cellular function
Monitoring and Assessment
While plasma zinc tests have limitations, you can monitor your progress through:
- Energy levels and overall vitality
- Immune function and infection frequency
- Sleep quality and mood stability
- Cognitive performance and mental clarity
The Future of Nutritional Health: Proactive Prevention
Addressing Global Challenges
As we face increasing environmental pressures and food system challenges, proactive nutritional supplementation becomes increasingly important. The combination of climate change, soil depletion, and modern lifestyle factors means that even health-conscious individuals may struggle to meet their nutritional needs through food alone.
Personalized Nutrition Approaches
The future of nutritional health lies in personalized approaches that consider:
- Individual genetic variations affecting nutrient needs
- Life stage and physiological demands
- Environmental exposures and stress levels
- Existing health conditions and medications
Building Resilience for Future Generations
By addressing nutritional deficiencies today, we can:
- Improve health outcomes for current and future generations
- Reduce healthcare costs associated with preventable diseases
- Build resilience against environmental and lifestyle challenges
- Support optimal human potential and quality of life
Conclusion: Taking Action for Optimal Health
The evidence is clear: zinc and magnesium deficiencies represent a significant threat to human health, affecting everything from immune function and cognitive development to energy production and disease prevention. These deficiencies begin in the womb and can impact health throughout the entire lifespan.
However, this challenge also represents an opportunity. By understanding the importance of these essential minerals and taking proactive steps to ensure adequate intake, we can build a foundation for optimal health and vitality. ThincZinc+ ULTRA provides a scientifically-formulated solution that addresses the unique challenges of modern nutrition, offering bioavailable forms of these critical nutrients in optimal ratios.
The choice is clear: we can either accept the nutritional limitations of our modern food system, or we can take control of our health through informed supplementation. For the sake of our health—from the womb and beyond—the time to act is now.